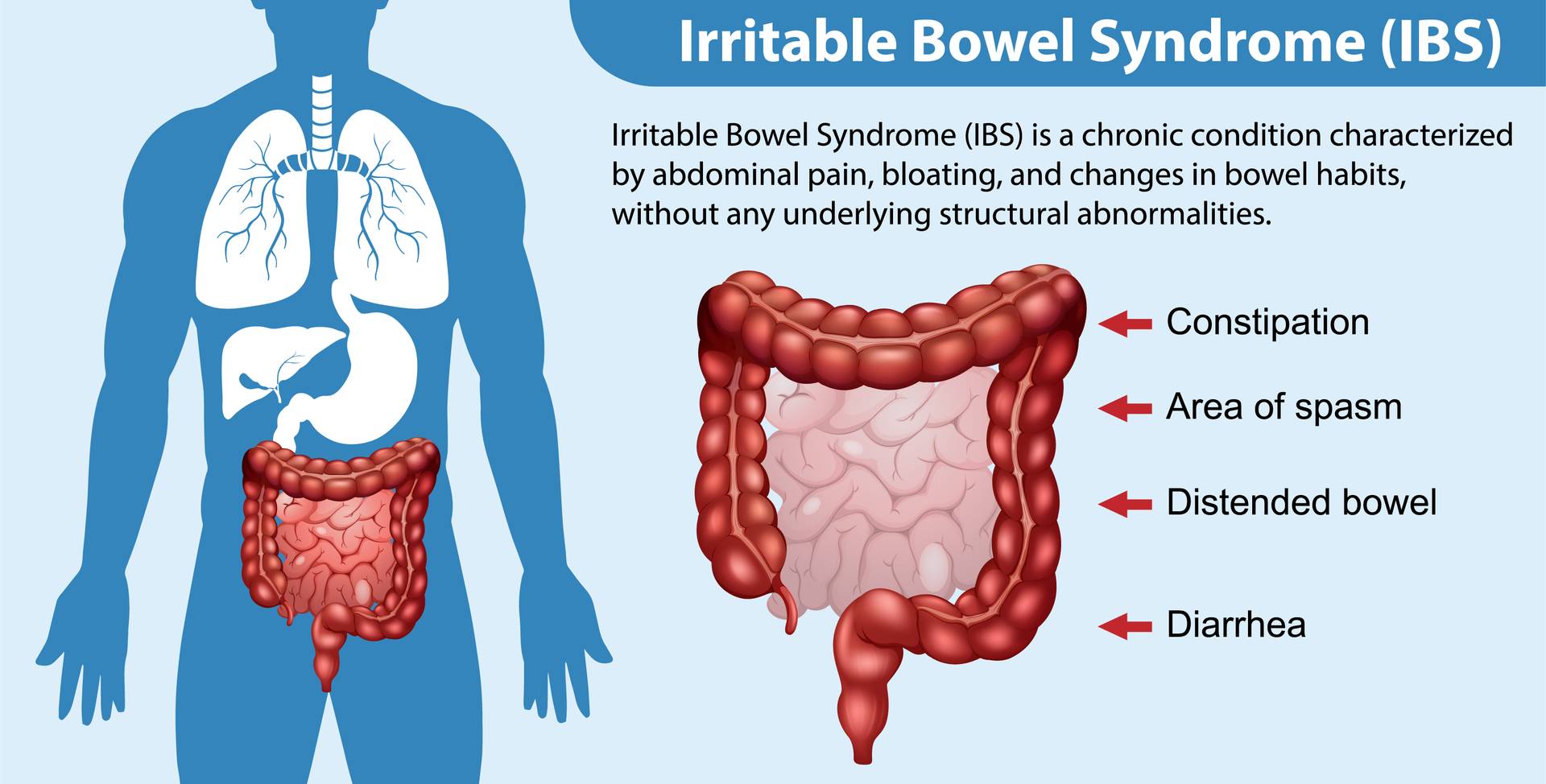

What is IBS?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder characterised by symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, changes in bowel habits (diarrhoea, constipation, or both), and discomfort in the abdomen.
Causes of Gut Health Issues and IBS
Gut health refers to the balance and optimal functioning of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the stomach, intestines, and colon. A healthy gut plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and overall well-being. Several factors can contribute to gut health issues and IBS, including:
- Dietary Factors: Poor dietary habits, such as excessive consumption of processed foods, high-fat foods, sugar, artificial additives, and low-fibre diets, can disrupt gut microbiota balance, impair digestion, and contribute to gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Stress and Lifestyle: Chronic stress, anxiety, lack of physical activity, inadequate sleep, and unhealthy lifestyle habits can affect gut motility, increase gut permeability, and exacerbate digestive symptoms in individuals prone to gut health issues and IBS.
- Gut Microbiome Imbalance: Alterations in the composition, diversity, and function of gut microbiota (dysbiosis) can impact gut health, immune responses, and gut-brain communication, leading to digestive disturbances, inflammation, and gut-related disorders like IBS.
- Genetic and Environmental Factors: Genetic predisposition, family history of digestive disorders, environmental factors (pollution, toxins), medications (antibiotics, NSAIDs), infections (gastroenteritis), and hormonal changes (menstrual cycle, hormonal fluctuations) can influence gut health and contribute to IBS development.
When to Seek Help
It is advisable to seek medical help if you experience persistent or severe symptoms related to gut health issues or IBS, such as:
- Chronic Abdominal Pain: Persistent or recurrent abdominal pain, cramping, discomfort, or bloating that affects daily activities, sleep, and quality of life.
- Altered Bowel Habits: Changes in bowel habits, including diarrhoea, constipation, alternating diarrhoea and constipation (mixed pattern), urgency, incomplete bowel movements, or mucus in stools.
- Digestive Symptoms: Frequent gas, bloating, distension, indigestion, heartburn, acid reflux, nausea, vomiting, or appetite changes.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss without dietary changes, intentional efforts, or underlying medical conditions.
- Blood in Stools: The presence of blood in stools, dark stools (melena), or rectal bleeding, which may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding or other serious conditions requiring medical evaluation.
- Persistent Fatigue: Chronic fatigue, weakness, lethargy, malaise, or decreased energy levels that are not relieved by rest or sleep.
What’s The Way Ahead?
Understanding the intricacies of your gut microbiome is paramount, as it plays a pivotal role in overall health. Taking a gut microbiome test can offer invaluable insights into its current state. By unravelling the microbial landscape within, you can pinpoint imbalances or deficiencies, allowing for tailored interventions such as dietary adjustments or probiotic supplementation. Armed with this knowledge, you can proactively nurture your gut and overall health.